Seven Lamps of Advocacy
Table of Contents
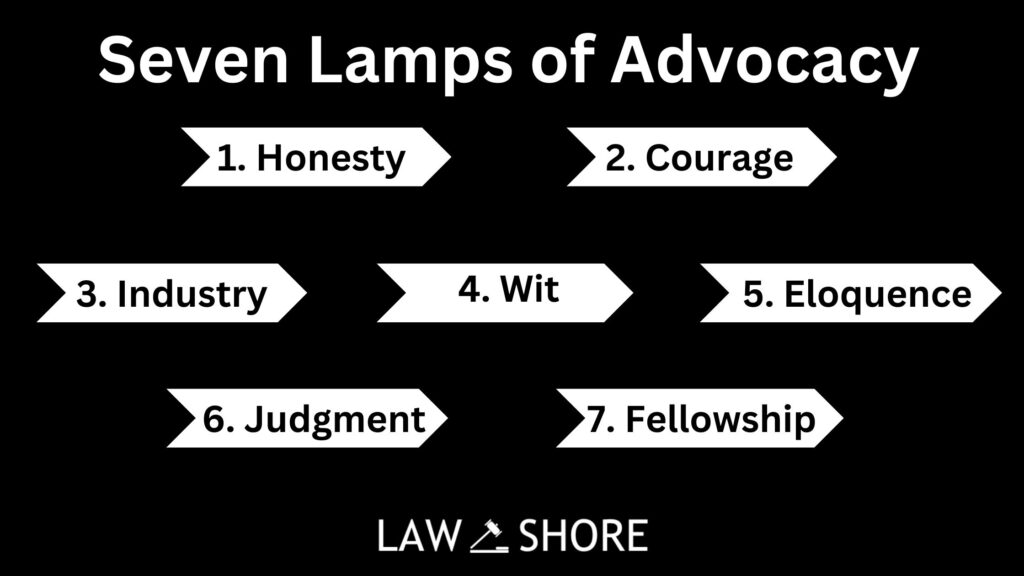
ToggleThe Seven Lamps of Advocacy, introduced by Edward Abbott Parry, highlights the key qualities every good advocate should have. These include honesty, courage, industry, wit, eloquence, judgment, and a sense of fellowship. Each of the seven principles guides advocates to do their job well while staying ethical. In this article, we’ll explore how these qualities help advocates succeed and make a positive impact on the legal system.
Advocacy is all about standing up for what is right, helping people get justice, and making sure the law works fairly for everyone. Advocates play an important role by guiding their clients through legal processes and defending their rights. They’re not just representing people, they’re also working to keep the legal system fair and trustworthy.

The Seven Lamps of Advocacy
1. Honesty
Honesty is the cornerstone of advocacy. It builds trust between an advocate and their client, peers, and the judicial system. An advocate must present facts truthfully, as deceit or misrepresentation can harm not just the case but also the justice system. A reputation for honesty enhances an advocate’s credibility and professional standing.
An advocate should always be honest with their client about the good and bad points of their case. This helps the client understand what to expect and builds trust and respect between them. Being truthful isn’t just about personal values, it shows dedication to fairness and justice. This is the most important of the Seven Lamps of Advocacy.
Key Points:
- Honest with clients: Clearly communicate the case’s strengths, weaknesses, and potential outcomes.
Honest with opponents: Avoid presenting misleading facts or deceptive strategies. - Honest with the law: Represent facts truthfully to uphold the integrity of the legal system.
2. Courage
Courage enables advocates to face challenges without fear, whether it’s arguing a difficult case or standing against societal prejudices. Advocates must have the courage to defend their client’s rights, even in the most contentious or high-stakes cases. Confidence stems from thorough preparation and a strong belief in the justice of their cause.
Courage also involves advocating for truth and justice, even when the opposition or circumstances are intimidating. It is essential for taking on controversial cases and standing firm in legal battles while respecting professional ethics.
Key Points:
- Fearless advocacy: Stand firm in court, even in challenging cases.
- Confidence: Build credibility through preparation and knowledge.
- Resilience: Overcome obstacles with determination and focus.
3. Industry
Hard work is a non-negotiable aspect of advocacy. Industry refers to the tireless effort and dedication an advocate invests in understanding the law, analyzing case details, and preparing arguments. Advocates must continuously update their knowledge as laws evolve and adapt to societal changes.
Being industrious ensures that no detail is overlooked, which can be critical to winning a case. It also reflects an advocate’s commitment to their client and their profession. Without sufficient preparation, even the most skilled advocate risks failure.
Key Points:
- Knowledge: Stay updated with current laws and precedents.
- Preparation: Dedicate time to thoroughly understand and analyze cases.
- Hard work: Consistently put in the effort to ensure effective representation.
4. Wit
Wit is the ability to think quickly and respond effectively under pressure. In the courtroom, where unexpected questions or challenges can arise, an advocate’s wit can make all the difference. It ensures that the advocate remains composed and resourceful.
A sharp wit also helps reduce mental strain and adds a layer of adaptability to the profession. Advocates who are quick thinkers can navigate complex cases more efficiently, filling gaps in arguments and addressing unforeseen issues.
Key Points:
- Quick thinking: Respond effectively to unexpected challenges.
- Presence of mind: Stay calm and resourceful in high-pressure situations.
- Creativity: Use wit to overcome obstacles and strengthen arguments.
5. Eloquence
Eloquence is the art of persuasive communication. Advocates must articulate their arguments clearly and effectively to leave a lasting impression on the judge, jury, and clients. Eloquence involves not only fluency in speech but also the ability to tailor the argument to resonate with the audience.
An advocate’s eloquence can sway decisions by presenting complex legal concepts in an understandable and impactful way. Effective communication builds trust and highlights the advocate’s confidence and professionalism.
Key Points:
- Fluency: Speak clearly and confidently without errors.
- Persuasion: Present arguments that influence the judge and audience.
- Impact: Use language effectively to strengthen the case’s position.
6. Judgment
Judgment involves analyzing the merits and demerits of a case to form a strategic approach. An advocate must anticipate potential questions and challenges while considering the consequences of every argument.
A good advocate views the case from multiple perspectives, ensuring they are prepared to counter opposing arguments effectively. Sound judgment enables an advocate to make informed decisions that align with the best interests of their client.
Key Points:
- Analysis: Understand both sides of the case to anticipate challenges.
- Preparation: Develop strategies to address questions from judges and opponents.
- Consequences: Evaluate the impact of arguments and evidence on the case.
7. Fellowship
Fellowship highlights respect and camaraderie among advocates and within the judicial system. While advocates may argue against each other in court, they must maintain professional relationships based on mutual respect.
Fellowship extends to respecting the judiciary as well. Advocates should always address judges and peers with decorum, which creates an environment of collaboration and trust that ultimately serves the cause of justice.
Key Points:
- Respect for peers: Maintain cordial relationships with fellow advocates.
- Respect for the judiciary: Address judges appropriately and honor their decisions.
- Professional ethics: Separate courtroom arguments from personal relationships.
Relevance in Modern Advocacy
One of the best things about the principles in The Seven Lamps of Advocacy is that they are still relevant in today’s legal world. Even though our society and technology keep changing, each of the seven principles continues to serve as a go-to guide for ethical and effective legal practice.
For example, honesty is crucial because courts and clients expect advocates to be transparent and truthful, especially in a time when misinformation can spread easily. Courage is also key, as they often deal with tough cases related to human rights, the environment, or unpopular causes, and they need to stand strong against public or institutional pressure.
Modern advocacy has evolved with the use of technology, which makes it easier for advocates to handle complex cases efficiently. At the same time, being well-prepared and thorough is still very important. In digital hearings, media interactions, and written submissions, Eloquence and wit matter more than ever, as they can influence how people see a case.
Good judgment is crucial for advocates as they deal with complex global rules and ethical challenges. Fellowship helps build a sense of community, encourages teamwork, and promotes ethical behavior in today’s competitive legal world. This is why the Seven Lamps continue to be a valuable guide for lawyers aiming to excel in modern practice.
Criticisms and Limitations
The Seven Lamps of Advocacy present a noble vision for the legal profession. But, some criticize them for idealising it. In today’s legal world, shaped by commercial pressures and adversarial tactics, strictly following these principles can be tough. For instance, balancing honesty with client confidentiality can create ethical challenges, and the principle of fellowship often struggles against the intense competition among advocates.
Also, cultural and systemic differences in legal systems worldwide can make it hard to apply these principles everywhere. Advocates often have to balance these ideals with the practical needs of their work, leading to compromises that weaken the original meaning of the principles.
Case Studies
Let’s explore some case studies that demonstrate how values like honesty, courage, and judgment have been exemplified in real-life scenarios:
1. Mahatma Gandhi:
Mahatma Gandhi’s time as a barrister showed his strong commitment to honesty and courage. When asked to manipulate the truth in a case, he chose to withdraw, which also shows his dedication to ethical advocacy.
2. Nani Palkhivala:
Famous for his eloquence and judgment, Palkhivala’s arguments in important cases like Kesavananda Bharati v. State of Kerala played a key role in shaping India’s constitutional law. His combination of powerful speech and sound judgment influenced judicial decisions.
3. Ruth Bader Ginsburg:
A modern example of courage and industry, Ginsburg’s advocacy for gender equality in the U.S. changed societal structures. Her eloquent arguments before the Supreme Court showed courage, judgment, and fellowship, as she worked to rally others to her cause.
Jurisprudence Behind 7 Lamps of Advocacy
The Seven Lamps of Advocacy, articulated by Edward Abbott Parry, provide a lasting guide for how advocates should act ethically and professionally. These principles, such as Honesty, Courage, Industry, Wit, Eloquence, Judgment, and Fellowship, are closely tied to justice, fairness, and professionalism.
In India, these qualities help advocates represent their clients effectively while protecting the integrity of the legal system. They also build trust and confidence in the rule of law.
Each of the seven “lamps” holds jurisprudential significance in India.
- Honesty highlights the advocates’s duty to present facts correctly (honestly), as required by the Bar Council of India.
- Courage underscores the need to fight for justice, even in politically or socially tough cases like Keshavananda Bharati v. State of Kerala, which questioned government power.
- Industry and diligence are essential for thorough legal research, as seen in cases like Maneka Gandhi v. Union of India, where advocates studied constitutional provisions deeply.
- Wit and Eloquence help lawyers explain complex legal issues clearly and convincingly, while good judgment helps them choose the best legal strategies.
- Fellowship promotes unity and respect within the legal fraternity, which is important for maintaining the dignity of the profession.
By sticking to and following these principles, Indian advocates help ensure justice is served and strengthen their role as guardians of the court and constitutional values.
The Seven Lamps of Advocacy continue to guide ethical legal practice. They make sure the path of justice stays fair and unbiased for each and every one.
Important Cases: Laws of 7 Lamps of Advocacy
1. Honesty
Case: State of Punjab v. Ramdev Singh (2004)
In this case, the Supreme Court stressed how important honesty is in the legal process, especially for lawyers. It reminded advocates that, as officers of the court, their main duty is to uphold truth and justice. The court said that honesty is the backbone of legal work, which helps ensure fairness when cases are presented. This is even more important in sensitive cases, like those about sexual offenses, where protecting the victim’s dignity and maintaining trust in the legal system is essential.
2. Courage
Case: Keshavananda Bharati v. State of Kerala (1973)
The Kesavananda Bharati case was all about great courage when the Supreme Court introduced the “basic structure doctrine.” The court stood firm, declaring that while Parliament can amend the Constitution, it cannot alter its basic structure. This bold decision safeguarded democracy and constitutional integrity, despite political pressure.
3. Industry
Case: Maneka Gandhi v. Union of India (1978)
The Court’s hard work redefined “personal liberty” under Article 21, ensuring that laws are fair, just, and reasonable. This case set a landmark precedent, which expanded fundamental rights and required the government to follow fair procedures. The advocates and judges worked tirelessly to protect personal freedom.
4. Wit
Case: Shreya Singhal v. Union of India (2015)
The Shreya Singhal v. Union of India case displayed wit and intellectual sharpness as the Court struck down Section 66A of the IT Act for being vague and unconstitutional. With intelligent reasoning, the judgment balanced freedom of speech with reasonable restrictions and protected citizens’ rights while ensuring public order.
5. Eloquence
Case: Kesavananda Bharati v. State of Kerala (1973)
This landmark case also reflected eloquence through its detailed reasoning and clear articulation of the “basic structure doctrine.” Over 68 days of profound legal debates, the lawyers and judges demonstrated the power of clear arguments in shaping constitutional law.
6. Judgment
Case: Mohori Bibee v. Dharmodas Ghose (1903)
The Mohori Bibee v. Dharmodas Ghose case exemplified sound judgment by ruling that contracts with minors are void from the start. This landmark decision laid the foundation for Indian contract law, showing prudence and clarity in determining the principles of legal capacity.
7. Fellowship
Case: Supreme Court Bar Association v. Union of India (1998)
The case highlighted fellowship by promoting mutual respect between the judiciary and the Bar. The judgment clarified that the judiciary could not directly punish advocates for misconduct, strengthening trust and cooperation within the legal community.
Conclusion
Let’s conclude this article by saying that the Seven Lamps of Advocacy highlight ethical and effective legal practices that define a good lawyer. These include honesty, courage, diligence, eloquence, judgment, wit, and professional fellowship. Together, they shape an advocate who is not only skilled but also upholds the fairness of the legal system. Even today, these principles guide advocates in handling the challenges of a constantly evolving legal world.
However, the daily challenges of being an advocate can make it hard to always live up to these ideals. But, the ethics mentioned here still serve as important goals. It keeps reminding them of their responsibility to justice and society. By understanding and adapting these core principles, advocates can better manage the challenges they face in their work. This allows them to maintain a strong sense of integrity while also handling the demands of their profession. It helps ensure that their legal practice reflects both expertise and moral character.
Explore Law Shore: law notes today and take the first step toward mastering the fundamentals of law with ease.

After Completing my LLB hons, I started writing content about legal concepts and case laws while practicing. I finally started Law Shore in 2024 with an aim to help other students and lawyers.